Damascus
| Damascus دِمَشق Dimashq |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
 Damascus Skyline |
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s): (Madinat Al-Yasmin) City of Jasmin | |||
 Damascus
|
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Syria | ||
| Governorates | Damascus Governorate, Capital City | ||
| Government | |||
| - Governor | Bishr Al Sabban | ||
| Area | |||
| - City | 109 km2 (42.1 sq mi) | ||
| - Urban | 848 km2 (327.4 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 680 m (2,231 ft) | ||
| Population (2007 est.[1]) | |||
| - City | 1,666,789 | ||
| - Metro | 4,850,500 | ||
| Time zone | EET (UTC+2) | ||
| - Summer (DST) | EEST (UTC+3) | ||
| Area code(s) | Country code: 963, City code: 11 | ||
| Demonym | Damascene | ||
| Sources: Damascus city area [2] | |||
Damascus (Arabic: دِمَشقُ Dimashq, commonly known as الشام ash-Shām also known as the "City of Jasmin" Arabic: مدينة الياسمين Madīnatul Yāsmīn) is the capital of Syria as well as one of the country's 14 governorates. The Damascus Governorate is ruled by a governor appointed by the Minister of Interior. In addition to being widely known as the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world, Damascus is a major cultural and religious center of the Levant.
Currently, the city has an estimated population of about 1,669,000.[1] Located in southwestern Syria, it is the center of a large metropolitan area of 4,8 million people.[3] Geographically embedded on the eastern foothills of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range 80 km (50 mi) inland from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea on a plateau 680 metres (2,200 ft) above sea-level, Damascus experiences a semi-arid climate due to the rain shadow effect. The Barada River flows through Damascus.
First settled in the 2nd millennium BC, it was chosen as the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate from 661–750. After the victory of the Abbasid dynasty, the seat of Islamic power was moved to Baghdad. Damascus saw a political decline throughout the Abbasid era, only to regain significant importance in the Ayyubid and Mamluk periods. During Ottoman rule, the city decayed completely while maintaining a certain cultural prestige. Today, it is the seat of the central government and all of the government ministries. Damascus was chosen as the 2008 Arab Capital of Culture.[4]
Contents |
Etymology

The name of Damascus first appeared in the geographical list of Thutmose III as T-m-ś-q in the 15th century BCE.[5] In Arabic, the city is called دمشق الشام (Dimashq al-Shām), although this is often shortened to either Dimashq or al-Shām by the citizens of Damascus, of Syria and other Arab neighbors. Al-Shām is an Arabic term for north and for Syria (Syria—particularly historical Greater Syria—is called Bilād al-Shām—بلاد الشام, "land of the north"—in Arabic.) The etymology of the ancient name "T-m-ś-q" is uncertain, but it is suspected to be pre-Semitic. It is attested as 𒁲𒈠𒊭𒅗 Dimašqa in Akkadian, 𒁲𒈠𒊭𒅗T-ms-ḳw in Egyptian, Dammaśq (דמשק) in Old Aramaic and Dammeśeq (דמשק) in Biblical Hebrew. The Akkadian spelling is the earliest attestation, found in the Amarna letters, from the 14th century BCE. Later Aramaic spellings of the name often include an intrusive resh (letter r), perhaps influenced by the root dr, meaning "dwelling". Thus, the Qumranic Darmeśeq (דרמשק), and Darmsûq (ܕܪܡܣܘܩ) in Syriac.[6][7] The English and Latin name of the city is "Damascus" which was imported from Greek: Δαμασκός, which originated in Aramaic: דרמשק; "a well-watered place".[8][9]
History
| Ancient City of Damascus* | |
|---|---|
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
.jpg) |
|
| State Party | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | i, ii, iii, iv, vi |
| Reference | 20 |
| Region** | Arab States |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 1979 (3rd Session) |
| * Name as inscribed on World Heritage List. ** Region as classified by UNESCO. |
|
Early settlement
Carbon-14 dating at Tell Ramad, on the outskirts of Damascus, suggests that the site may have been occupied since the second half of the seventh millennium BC, possibly around 6300 BC.[10] However, evidence of settlement in the wider Barada basin dating back to 9000 BC exists, although no large-scale settlement was present within Damascus walls until the second millennium BC. The city is considered by historians to be the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world.[11]
The Damascus region, as well as the rest of Syria, became a battleground circa 1260 BC, between the Hittites from the north and the Egyptians from the south,[12] ending with a signed treaty between Hattusili and Ramsis II where the former handed over control of the Damascus area to Ramesses II in 1259 BC.[12] The arrival of the Sea Peoples, around 1200 BC, marked the end of the Bronze Age in the region and brought about new development of warfare.[13] Damascus was only the peripheral part of this picture which mostly affected the larger population centers of ancient Syria. However, these events had contributed to the development of Damascus as a new influential center that emerged with the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age.[13]
Damascus is mentioned in Genesis 14:15 as existing at the time of the War of the Kings.[14] (However, the verse can also be understood to mean that Damascus existed when Genesis was written – by tradition around the 13th century BC, and several centuries later according to some scholars – regardless of whether Damascus existed at the time of the War of the Kings.) According to the 1st century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus in his twenty-one volume Antiquities of the Jews, Damascus (along with Trachonitis), was founded by Uz, the son of Aram. Elsewhere, he stated:
Nicolaus of Damascus, in the fourth book of his History, says thus: "Abraham reigned at Damascus, being a foreigner, who came with an army out of the land above Babylon, called the land of the Chaldeans: but, after a long time, he got him up, and removed from that country also, with his people, and went into the land then called the land of Canaan, but now the land of Judea, and this when his posterity were become a multitude; as to which posterity of his, we relate their history in another work. Now the name of Abraham is even still famous in the country of Damascus; and there is shown a village named from him, The Habitation of Abraham.
Damascus was part of the ancient province of Amurru in the Hyksos Kingdom, from 1720 to 1570 BC.[15] Some of the earliest Egyptian records are from the 1350 BC Amarna letters, when Damascus-(called Dimasqu) was ruled by king Biryawaza.
Aram-Damascus
Damascus is not documented as an important city until the arrival of the Aramaeans, Semitic nomads from Mesopotamia, in the 11th century BCE. By the start of the 1st millennium BC, several Aramaic kingdoms were formed, as Aramaeans abandoned their nomadic lifestyle and formed federated tribal states. One of these kingdoms was Aram-Damascus centered around its capital Damascus.[16] The Aramaeans who entered the city without battle, adopted the name "Dimashqu" for their new home. Noticing the agricultural potential of the still-undeveloped and sparsely populated area,[17] they established the water distribution system of Damascus by constructing canals and tunnels which maximized the efficiency of the river Barada. The same network was later improved by the Romans and the Umayyads, and still forms the basis of the water system of the old part of the city today.[18] The Aramaeans initially turned Damascus into an outpost of a loose federation of Aramaean tribes, known as Aram-Zobah, based in the Beqaa Valley.[17]

The city would gain preeminence in southern Syria when Ezron, the claimant to Aram-Zobah's throne who was denied kingship of the federation, fled Beqaa and captured Damascus by force in 965 BC. Ezron overthrew the city's tribal governor and founded the independent entity of Aram-Damascus. As this new state expanded south, it prevented the Kingdom of Israel from spreading north and the two kingdoms soon clashed as they both sought to dominate trading hegemony in the east.[17] Under Ezron's grandson, Ben-Hadad I (880–841 BC), and his successor Hazael, Damascus annexed Bashan (modern-day Hauran region), and went on the offensive with Israel. This conflict continued until the early 8th century BC when Ben-Hadad II was captured by Israel after unsuccessfully besieging Samaria. As a result, he granted Israel trading rights in Damascus.[19]
Another possible reason for the treaty between Aram-Damascus and Israel was the common threat of the Neo-Assyrian Empire which was attempting to expand into the Mediterranean coast. In 853 BC, King Hadadezer of Damascus led a Levantine coalition, that included forces from the northern Aram-Hamath kingdom and troops supplied by King Ahab of Israel, in the Battle of Qarqar against the Neo-Assyrian army. Aram-Damascus came out victorious, temporarily preventing the Assyrians from encroaching into Syria. However, after Hadadzezer was killed by his successor, Hazael II, the Levantine alliance collapsed. Aram-Damascus attempted to invade Israel, but was interrupted by the renewed Assyrian invasion. Hazael ordered a retreat to the walled part of Damascus while the Assyrians plundered the remainder of the kingdom. Unable to enter the city, they declared their supremacy in the Hauran and Beqa'a valleys.[19]
By the 8th century BC, Damascus was practically engulfed by the Assyrians and entered a dark age. Nonetheless, it remained the economic and cultural center of the Near East as well as the Arameaen resistance. In 727, a revolt took place in the city, but was put down by Assyrian forces. After Assyria went on a wide-scale campaign of quelling revolts throughout Syria, Damascus became totally subjugated by their rule. A positive effect of this was stability for the city and benefits from the spice and incense trade with Arabia. However, Assyrian authority was dwindling by 609–605 BC, and Syria-Palestine was falling into the orbit of Pharaoh Necho II's Egypt. In 572, all of Syria had been conquered by the Neo-Babylonians, but the status of Damascus under Babylon is relatively unknown.[20]
Antiquity

Damascus was conquered by Alexander the Great. After the death of Alexander in 323 BCE, Damascus became the site of a struggle between the Seleucid and Ptolemaic empires. The control of the city passed frequently from one empire to the other. Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander's generals, made Antioch the capital of his vast empire, which led to the decline of Damascus' importance compared with new Seleucid cities such as Latakia in the north. Later, Demetrius III Philopator rebuilt the city according to the Greek hippodamian system and renamed it "Demetrias".
In 64 BCE, the Roman general Pompey annexed the western part of Syria. The Romans occupied Damascus and subsequently incorporated it into the league of ten cities known as the Decapolis because it was considered such an important center of Greco-Roman culture. According to the New Testament, Saint Paul was on the road to Damascus when he received a vision, was struck blind and as a result converted to Christianity. In the year 37, Roman Emperor Caligula transferred Damascus to Nabataean control by decree. The Nabataean king Aretas IV Philopatris ruled Damascus from his capital Petra. However, around the year 106, Nabataea was conquered by the Romans, and Damascus returned to Roman control.
Damascus became a metropolis by the beginning of the second century and in 222 it was upgraded to a colonia by the Emperor Septimius Severus. During the Pax Romana, Damascus and the Roman province of Syria in general began to prosper. Damascus's importance as a caravan city was evident with the trade routes from southern Arabia, Palmyra, Petra, and the silk routes from China all converging on it. The city satisfied the Roman demands for eastern luxuries.
Little remains of the architecture of the Romans, but the town planning of the old city did have a lasting effect. The Roman architects brought together the Greek and Aramaean foundations of the city and fused them into a new layout measuring approximately 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) by 750 metres (2,460 ft), surrounded by a city wall. The city wall contained seven gates, but only the eastern gate (Bab Sharqi) remains from the Roman period. Roman Damascus lies mostly at depths of up to five meters (16.4 ft) below the modern city.
The old borough of Bab Tuma was developed at the end of the Roman/Byzantine era by the local Eastern Orthodox community. According to the Acts of the Apostles, Saint Paul and Saint Thomas both lived in that neighborhood. Roman Catholic historians also consider Bab Tuma to be the birthplace of several Popes such as John V and Gregory III.
Islamic Arab era
.jpg)
After most of the Syrian countryside was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate during the reign of Caliph Umar, Damascus itself was conquered by the Muslim-Arab general Khalid ibn al-Walid in September–August 635 CE. His army had previously attempted to capture the city in April 634, but without success.[21] With Damascus now in Muslim-Arab hands, the Byzantines, alarmed at the loss of their most prestigious city in the Near East, had decided to wrest back control of it. Under Emperor Heraclius, the Byzantines fielded an army superior to that of the Rashidun in manpower. They advanced into southern Syria during the spring of 636 and consequently Khalid ibn al-Walid's forces withdrew from Damascus to prepare for renewed confrontation.[22] In August, the two powers met along the Yarmouk River where they a fought a major battle which ended in a decisive Muslim victory, solidifying the latter's rule in Syria and Palestine.[23]
While the Muslims administrated the city, the population of Damascus remained mostly Christian—Eastern Orthodox and Monophysite—with a growing community of Muslims from Mecca, Medina, and the Syrian Desert.[24] The governor assigned to the city which had been chosen as the capital of Islamic Syria was Mu'awiya I. After the murder of Caliph Ali in 661, Mu'awiya installed himself as the caliph of the expanding Islamic empire. Because of the vast amounts of assets his clan, the Ummayads, owned in the city and because of its traditional economic and social links with the Hijaz as well as the Christian Arab tribes of the region, Mu'awiya established Damascus as the capital of the entire Caliphate.[25] With the ascension of Caliph Abd al-Malik in 685, an Islamic coinage system was introduced and all of the surplus revenue of the Caliphate's provinces were forwarded to the treasury of Damascus. Arabic was also established as the official language, giving the Muslim minority of the city an advantage over the Aramaic-speaking Christians in administrative affairs.[26] It is critical to note that, at the time Damascus was conquered by the Muslims, the majority of Arabs were either pagans or Christians. Damascus itself was predominantly Aramaic with Arab speaking people.
Abd al-Malik's successor, al-Walid initiated construction of the Grand Mosque of Damascus (known as the Umayyad Mosque) in 706. The site originally had been the Christian Cathedral of St. John and the Muslims maintained the building's dedication to John the Baptist.[27] By 715, the mosque was complete. Al-Walid died that same year and he was succeeded at first by Suleiman ibn Abd al-Malik and then by Umar II, who each ruled for brief periods before the reign of Hisham in 724. With these successions, the status of Damascus was gradually weakening as Suleiman had chosen Ramla as his residence and later Hisham chose Rusafa. Following the murder of the latter in 743, the Caliphate of the Umayyads — which by then stretched from Spain to India— was crumbling as a result of widespread revolts. During the reign of Marwan II in 744, the capital of the empire was relocated to Harran in the northern Jazira region.[28]

On August 25, 750, the Abbasids, having already beaten the Umayyads in the Battle of the Zab in Iraq, conquered Damascus after facing little resistance. With the heralding of the Abbasid Caliphate, Damascus became eclipsed and subordinated by Baghdad, the new Islamic capital. Within the first six months of Abbasid rule, revolts began erupting in the city, albeit too isolated and unfocused to present a viable threat. Nonetheless, the last of the prominent Umayyads were executed, the traditional officials of Damascus ostracized, and army generals from the city were dismissed. Afterward, the Umayyad family cemetery was desecrated and the city walls were torn down, reducing Damascus into a provincial town of little importance. It roughly disappeared from written records for the next century and the only significant improvement of the city was the Abbasid-built treasury dome in the Umayyad Mosque in 789. In 811, distant remnants of the Umayyad dynasty staged a strong uprising in Damascus that was eventually put down.[29]
Ahmad ibn Tulun, a dissenting Turkish governor appointed by the Abbasids, conquered Syria, including Damascus, from his overlords in 878-79. In an act of respect for the previous Umayyad rulers, he erected a shrine on the site of Mu'awiya's grave in the city. Tulunid rule of Damascus was brief, lasting only until 906 before being replaced by the Qarmatians who were adherents of Shia Islam. Due to their inability to control the vast amount of land they occupied, the Qarmatians withdrew from Damascus and a new dynasty, the Ikhshidids, took control of the city. They maintained the independence of Damascus from the Arab Hamdanid dynasty of Aleppo and the Baghdad-based Abbasids until 967. A period of instability in the city followed, with a Qarmatian raid in 968, a Byzantine raid in 970, and increasing pressures from the Fatimids in the south and the Hamdanids in the north.[30]
The Shia Fatimids gained control in 970, inflaming hostilities between them and the Sunni Arabs of the city who frequently revolted. A Turk, Alp Takin drove out the Fatimids five years later, and through diplomacy, prevented the Byzantines from attempting to annex the city. However, by 777, the Fatimids under Caliph al-Aziz, wrested back control of the city and tamed Sunni dissidents. The Arab geographer, al-Muqaddasi, visited Damascus in 985, remarking that the architecture and infrastructure of the city was "magnificent," but living conditions were awful. Under al-Aziz, the city saw a brief period of stability that ended with the reign of al-Hakim (996–1021). In 998, Hundreds of Damascene leaders were rounded up and executed by him for incitement. Three years after al-Hakim's mysterious disappearance, the Arab tribes of southern Syria formed an alliance to stage a massive rebellion against the Fatimids, but they were crushed by the Fatimid Turkish governor of Syria and Palestine, Anushtakin al-Duzbari, in 1029. This victory gave the latter mastery over Syria, displeasing his Fatimid overlords, but gaining the admiration of Damascus' citizens. He was exiled by Fatimid authorities to Aleppo where he died in 1041.[31] From that date to 1063, there are no known records of the city's history. By then, Damascus lacked a city administration, had an enfeebled economy, and a greatly reduced population.[32]
Seljuk and Ayyubid rule

With the arrival of the Seljuk Turks in the late 11th century, Damascus again became the capital of independent states. It was ruled by Abu Sa'id Taj ad-Dawla Tutush I starting in 1079 and he was succeeded by his son Abu Nasr Duqaq in 1095. The Seljuks established a court in Damascus and a systematic reversal of Shia inroads in the city. The city also saw an expansion of religious life through private endowments financing religious institutions (madrasas) and hospitals (maristans). Damascus soon became one of the most important centers of propagating Islamic thought in the Muslim world. After Duqaq's death in 1104, his mentor (atabeg), Tughtekin, took control of Damascus and the Burid line of the Seljuk dynasty. Under Duqaq and Tughtekin, Damascus experienced stability, elevated status and a revived role in commerce. In addition, the city's Sunni majority enjoyed being a part of the larger Sunni framework effectively governed by various Turkic dynasties who in turn were under the moral authority of the Baghdad-based Abbasids.[33]
While the rulers of Damascus were preoccupied in conflict with their fellow Seljuks in Aleppo and Diyarbakir, the Crusaders, who arrived in the Levant in 1097, conquered Jerusalem, Mount Lebanon and Palestine. Duqaq seemed to have been content with Crusader rule as a buffer between his dominion and the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. Tughtekin, however, saw the Western invaders as a viable threat to Damascus which, at the time, nominally included Hims, the Beqaa Valley, Hauran, and the Golan Heights a part of its territories. With military support from Sharaf al-Din Mawdud of Mosul, Tugthekin managed to halt Crusader raids in the Golan and Hauran. Mawdud was assassinated in the Umayyad Mosque in 1109, depriving Damascus of northern Muslim backing and forcing Tughtekin to agree to a truce with the Crusaders in 1110.[34]
Following Tughtakin's death in 1128, his son, Taj al-Din Buri, became the nominal ruler of Damascus. Coincidentally, the Seljuk prince of Mosul, Imad al-Din Zengi, took power in Aleppo and gained a mandate from the Abbasids to extend his authority to Damascus. In 1129, around 6,000 Isma'ili Muslims were killed in the city along with their leaders. The Sunnis were provoked by rumors alleging there was a plot by the Isma'ilis, who controlled the strategic fort at Baniyas, to aid the Crusaders in capturing Damascus in return for control of Tyre. Soon after the massacre, the Crusaders aimed to take advantage of the unstable situation and launch an assault against Damascus with nearly 60,000 troops. However, Buri allied with Zengi and managed to prevent their army from reaching the city.[35] Buri was assassinated by Isma'ili agents in 1132; he was succeeded by his son, Shams al-Mulk Isma'il who ruled tyrannically until he himself was murdered in 1135 on secret orders from his mother, Safwat al-Mulk Zumurrud; Isma'il's brother, Shihab al-Din Mahmud, replaced him. Meanwhile, Zengi, intent on putting Damascus under his control, married Safwat al-Mulk in 1138. Mahmud's reign then ended in 1139 after he was killed for relatively unknown reasons by members of his family. Mu'in al-Din Unur, his mamluk ("slave soldier") took effective power of the city, prompting Zengi—with Safwat al-Mulk's backing—to lay siege against Damascus the same year. In response, Damascus allied with the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem to resist Zengi's forces. Consequently, Zengi withdrew his army and focused on campaigns against northern Syria.[36]

In 1144 Zengi conquered Edessa, a crusader stronghold, which led to a new crusade from Europe in 1148. In the meantime Zengi was assassinated and his territory was divided among his sons, one of whom, Nur ad-Din, emir of Aleppo, made an alliance with Damascus. When the European crusaders arrived, they and the nobles of Jerusalem agreed to attack Damascus. Their siege, however, was a complete failure. When the city seemed to be on the verge of collapse, the crusader army suddenly moved against another section of the walls, and were driven back. By 1154, Damascus was firmly under Nur ad-Din's control.[37]
In 1164, King Amalric of Jerusalem invaded Fatimid Egypt, which requested help from Nur ad-Din. The Nur ad-Din sent his general Shirkuh, and in 1166 Amalric was defeated at the Battle of al-Babein. When Shirkuh died in 1169, he was succeeded by his nephew Yusuf, better known as Saladin, who defeated a joint crusader-Byzantine siege of Damietta.[38] Saladin eventually overthrew the Fatimid caliphs and established himself as Sultan of Egypt. He also began to assert his independence from Nur ad-Din, and with the death of both Amalric and Nur ad-Din in 1174, he was well-placed to begin exerting control over Damascus and Nur ad-Din's other Syrian possessions.[39] In 1177 Saladin was defeated by the crusaders at the Battle of Montgisard, despite his numerical superiority.[40] Saladin also besieged Kerak in 1183, but was forced to withdraw. He finally launched a full invasion of Jerusalem in 1187, and annihilated the crusader army at the Battle of Hattin in July. Acre fell to Saladin soon after, and Jerusalem itself was captured in October. These events shocked Europe, resulting in the Third Crusade in 1189, led by Richard I of England, Philip II of France and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, though the last drowned en route.[41]
The surviving crusaders, joined by new arrivals from Europe, put Acre to a lengthy siege which lasted until 1191. After re-capturing Acre, Richard defeated Saladin at the Battle of Arsuf in 1191 and the Battle of Jaffa in 1192, recovering most of the coast for the Christians, but could not recover Jerusalem or any of the inland territory of the kingdom. The crusade came to an end peacefully, with the Treaty of Ramla in 1192. Saladin allowed pilgrimages to be made to Jerusalem, allowing the crusaders to fulfill their vows, after which they all returned home. The native crusader barons set about rebuilding their kingdom from Acre and the other coastal cities.[42]
Saladin died in 1193, and there were frequent conflicts between different Ayyubid sultans ruling in Damascus and Cairo. Damascus was the capital of independent Ayyubid rulers between 1193 and 1201, from 1218 to 1238, from 1239 to 1245, and from 1250 to 1260. At other times it was ruled by the Ayyubid rulers of Egypt. Damascus steel gained a legendary reputation among the Crusaders, and patterned steel is still "damascened". The patterned Byzantine and Chinese silks available through Damascus, one of the Western termini of the Silk Road, gave the English language "damask".
Mamluk period
Ayyubid rule (and independence) came to an end with the Mongol invasion of Syria in 1260, and following the Mongol defeat at Ain Jalut in the same year, Damascus became a provincial capital of the Mamluk Empire, ruled from Egypt, following the Mongol withdrawal. The Black Death of 1348–1349 wiped out perhaps as much as half of the city’s population.[43]
In 1400 Timur, the Turco-Mongol conqueror, besieged Damascus. The Mamluk sultan dispatched a deputation from Cairo, including Ibn Khaldun, who negotiated with him, but after their withdrawal he put the city to sack. The Umayyad Mosque was burnt and men and women taken into slavery. A huge number of the city's artisans were taken to Timur's capital at Samarkand. These were the luckier citizens: many were slaughtered and their heads piled up in a field outside the north-east corner of the walls, where a city square still bears the name burj al-ru'us, originally "the tower of heads".
Rebuilt, Damascus continued to serve as a Mamluk provincial capital until 1516.
Ottoman rule



In early 1516, the Ottoman Turks, wary of the danger of an alliance between the Mamluks and the Persian Safavids, started a campaign of conquest against the Mamluk sultanate. On 21 September, the Mamluk governor of Damascus fled the city, and on 2 October the khutba in the Umayyad mosque was pronounced in the name of Selim I. The day after, the victorious sultan entered the city, staying for three months. On 15 December, he left Damascus by Bab al-Jabiya, intent on the conquest of Egypt. Little appeared to have changed in the city: one army had simply replaced another. However, on his return in October 1517, the sultan ordered the construction of a mosque, tekkiye and mausoleum at the shrine of Shaikh Muhi al-Din ibn Arabi in al-Salihiyah. This was to be the first of Damascus' great Ottoman monuments.
The Ottomans remained for the next 400 years, except for a brief occupation by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt from 1832 to 1840. Because of its importance as the point of departure for one of the two great Hajj caravans to Mecca, Damascus was treated with more attention by the Porte than its size might have warranted — for most of this period, Aleppo was more populous and commercially more important. In 1560 the Tekkiye al-Sulaimaniyah, a mosque and khan for pilgrims on the road to Mecca, was completed to a design by the famous Ottoman architect Mimar Sinan, and soon afterwards a madrasa was built adjoining it.

Under Ottoman rule, Christians and Jews were considered dhimmis and were allowed to practice their religious precepts. The Damascus affair that took place in 1840 was an incident in which the accusation of ritual murder was brought against members of the Jewish community of Damascus. In addition the massacre of Christians in 1860 was also one of the most notorious incidents of these centuries, when fighting between Druze and Maronites in Mount Lebanon spilled over into the city. Several thousand Christians were killed, with many more being saved through the intervention of the Algerian exile Abd al-Qadir and his soldiers (three days after the massacre started), who brought them to safety in Abd al-Qadir's residence and the citadel. The Christian quarter of the old city (mostly inhabited by Catholics), including a number of churches, was burnt down. The Christian inhabitants of the notoriously poor and refractory Midan district outside the walls (mostly Orthodox) were, however, protected by their Muslim neighbours.
American Missionary E.C. Miller records that in 1867 the population of the city was 'about' 140,000, of whom 30,000 where Christians, 10,000 Jews and 100,000 'Mohammedans' with fewer than 100 Protestant Christians.[44]
Modern

In the early years of the twentieth century, nationalist sentiment in Damascus, initially cultural in its interest, began to take a political colouring, largely in reaction to the turkicisation programme of the Committee of Union and Progress government established in Istanbul in 1908. The hanging of a number of patriotic intellectuals by Jamal Pasha, governor of Damascus, in Beirut and Damascus in 1915 and 1916 further stoked nationalist feeling, and in 1918, as the forces of the Arab Revolt and the British army approached, residents fired on the retreating Turkish troops.

On 1 October 1918, T. E. Lawrence entered Damascus, the third arrival of the day, the first being the 3rd Australian Light Brigade, led by Major A.C.N. 'Harrry' Olden.[45] Two days later, October 3, 1918, the forces of the Arab revolt led by Prince Faysal also entered Damascus.[46] A military government under Shukri Pasha was named and Faisal ibn Hussein was proclaimed king of Syria. Political tension rose in November 1917, when the new Bolshevik government in Russia revealed the Sykes-Picot Agreement whereby Britain and France had arranged to partition the Arab east between them. A new Franco-British proclamation on 17 November promised the "complete and definitive freeing of the peoples so long oppressed by the Turks." The Syrian National Congress in March adopted a democratic constitution. However, the Versailles Conference had granted France a mandate over Syria, and in 1920 a French army commanded by the General Mariano Goybet crossed the Anti-Lebanon Mountains, defeated a small Syrian defensive expedition at the Battle of Maysalun and entered Damascus. The French made Damascus capital of their League of Nations Mandate of Syria.
When in 1925 the Druze revolt in the Hauran spread to Damascus, the French suppressed it brutally, bombing and shelling the city on May 9, 1926. As a result the area of the old city between Al-Hamidiyah Souq and Medhat Pasha Souq was burned to the ground, with many deaths, and has since then been known as al-Hariqa ("the fire"). The old city was surrounded with barbed wire to prevent rebels infiltrating from the Ghouta, and a new road was built outside the northern ramparts to facilitate the movement of armored cars.
On 21 June 1941, Damascus was captured from the Vichy French forces by the Allies during the Syria-Lebanon campaign. On May 29, 1945, the French once more bombed Damascus, but on this occasion British forces intervened and the French agreed to withdraw, thus leading to the full independence of Syria in 1946 . Damascus remained the capital.
Geography

Damascus lies about 80 km (50 mi) inland from the Mediterranean Sea, sheltered by the Anti-Lebanon Mountains. It lies on a plateau 680 metres (2,230 ft) above sea-level.
.jpg)
The old city of Damascus, enclosed by the city walls, lies on the south bank of the river Barada which is almost dry (3 cm left). To the south-east, north and north-east it is surrounded by suburban areas whose history stretches back to the Middle Ages: Midan in the south-west, Sarouja and Imara in the north and north-west. These districts originally arose on roads leading out of the city, near the tombs of religious figures. In the nineteenth century outlying villages developed on the slopes of Jabal Qasioun, overlooking the city, already the site of the al-Salihiyah district centred around the important shrine of Sheikh Muhi al-Din ibn Arabi. These new districts were initially settled by Kurdish soldiery and Muslim refugees from the European regions of the Ottoman Empire which had fallen under Christian rule. Thus they were known as al-Akrad (the Kurds) and al-Muhajirin (the migrants). They lay two to three kilometres (2 mi) north of the old city.
From the late nineteenth century on, a modern administrative and commercial centre began to spring up to the west of the old city, around the Barada, centred on the area known as al-Marjeh or the meadow. Al-Marjeh soon became the name of what was initially the central square of modern Damascus, with the city hall on it. The courts of justice, post office and railway station stood on higher ground slightly to the south. A Europeanised residential quarter soon began to be built on the road leading between al-Marjeh and al-Salihiyah. The commercial and administrative centre of the new city gradually shifted northwards slightly towards this area.
In the twentieth century, newer suburbs developed north of the Barada, and to some extent to the south, invading the Ghouta oasis. From 1955 the new district of Yarmouk became a second home to thousands of Palestinian refugees. City planners preferred to preserve the Ghouta as far as possible, and in the later twentieth century some of the main areas of development were to the north, in the western Mezzeh district and most recently along the Barada valley in Dummar in the northwest and on the slopes of the mountains at Berze in the north-east. Poorer areas, often built without official approval, have mostly developed south of the main city.
Damascus used to be surrounded by an oasis, the Ghouta region (الغوطة al-ġūṭä), watered by the Barada river. The Fijeh spring, west along the Barada valley, used to provide the city with drinking water. The Ghouta oasis has been decreasing in size with the rapid expansion of housing and industry in the city and it is almost dry. It has also become polluted due to the city's traffic, industry, and sewage.
Climate
Damascus has a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification BSh), due to the rain shadow effect of the Anti-Lebanon mountains[47] and the prevailing ocean currents. Summers are dry and hot with less humidity. Winters are mild and comparatively rainy, sometimes snowy. January maximum and minimum temperatures are 12.6 °C (54.7 °F) and 0.4 °C (32.7 °F), lowest ever recorded being −13.5 °C (8 °F). The July maximum and minimum temperature are 36.5 °C (97.7 °F) and 16.9 °C (62.4 °F), with the highest ever recorded being 45.5 °C (114 °F). Annual rainfall is around 134 mm (5.3 in), occurring from November to March.
| Climate data for Damascus | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.6 (54.7) |
14.8 (58.6) |
18.9 (66) |
24.5 (76.1) |
29.7 (85.5) |
34.2 (93.6) |
36.5 (97.7) |
36.2 (97.2) |
33.4 (92.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
20.3 (68.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.4 (32.7) |
1.3 (34.3) |
3.7 (38.7) |
7.0 (44.6) |
10.5 (50.9) |
14.2 (57.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
16.5 (61.7) |
13.0 (55.4) |
8.9 (48) |
4.0 (39.2) |
1.3 (34.3) |
8.1 (46.6) |
| Rainfall mm (inches) | 47.9 (1.886) |
32.7 (1.287) |
16.9 (0.665) |
7.9 (0.311) |
6.3 (0.248) |
3.4 (0.134) |
0.4 (0.016) |
0 (0) |
5.2 (0.205) |
17.1 (0.673) |
31.4 (1.236) |
45.8 (1.803) |
215.00 (8.4646) |
| Avg. rainy days | 16 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 78 |
| Source: World Meteorological Organisation (UN) [48] | |||||||||||||
Economy

The historical role that Damascus played as an important trade center has changed in recent years due to political development in the region as well as the development of modern trade.[49] Most goods produced in Damascus, as well as in Syria, are distributed to Countries of the Arabian peninsula.[49] Damascus also holds an annual international trade exposition in the fall since 1955.[50]
Damascus has the potential for a highly successful tourism industry. The abundance of cultural wealth in Damascus has been modestly employed since the late 1980s with the development of many accommodation and transportation establishments and other related investments.[49] Since the early 2000s, numerous boutique hotels and bustling cafes opened in the old city which attract plenty of European tourists and Damascenes alike.[51]
The real-estate sector is booming in Damascus. Real-estate adviser Cushman & Wakefield listed Damascus office space as the eighth most expensive in the world in 2009.[51] The office market in Damascus is rather immature and the demand for premium office space surpasses supply. However, new supply of office space is expected to be delivered in 2009.[52] Damascus is home to a wide range of industrial activity, such as Textile, food processing, Cement and various Chemical industries.[49] The majority of factories are run by the state, however, limited privatization in addition to economic activities let by the private sector were permitted starting in the early 2000s with the liberalization of trade that took place .[49] Traditional handcrafts and artisan copper engraving are still produced in the old city.[49]
The Damascus stock exchange formally opened for trade in March 2009, and the exchange is the only stock exchanges in Syria.[53] It is currently located in the Barzeh district, within Syria's financial markets and securities commission. Its final home is to be the upmarket business district of Yaafur.[54]
Demographics
The population of Damascus in 2009 was 4,850,500 according to the 2009 official census conducted by the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) in Syria.[55] However, according to the 2007 estimates released by the CBS.
The metropolitan area of Damascus includes the cities of Duma, Harasta, Darayya, Al-Tall and Jaramana. The lack of official population statistics in these cities makes it hard to estimate the population of the wider metropolitan area around Damascus,

People
The majority of the population in Damascus came as a result of rural-urban migration.
Religion
The majority of the inhabitants of Damascus—about 75%—are Sunni Muslims. It is believed that there are more than 2,000 mosques in Damascus, the most well-known being the Umayyad Mosque.[56] Christians-especially Syriac-Assyrians-represent 15% of the population, and there a number of Christian districts, such as Bab Tuma, Kassaa, and Ghassani, with many churches, most notably the ancient Chapel of Saint Paul. There is a small Jewish community namely in what is called Haryet il-yahoud the Jewish quarter, they are the remnants of an ancient and much larger Jewish presence in Syria, dating back at least to Roman times, if not before to the time of King David.[57]
Historical sites


Damascus has a wealth of historical sites dating back to many different periods of the city's history. Since the city has been built up with every passing occupation, it has become almost impossible to excavate all the ruins of Damascus that lie up to 8 feet (2.4 m) below the modern level. The Citadel of Damascus is located in the northwest corner of the Old City. The Street Called Straight (referred to in the conversion of St. Paul in Acts 9:11), also known as the Via Recta, was the decumanus (East-West main street) of Roman Damascus, and extended for over 1,500 metres (4,900 ft). Today, it consists of the street of Bab Sharqi and the Souk Medhat Pasha, a covered market. The Bab Sharqi street is filled with small shops and leads to the old Christian quarter of Bab Tuma (St. Thomas's Gate). Medhat Pasha Souq is also a main market in Damascus and was named after Medhat Pasha, the Ottoman governor of Syria who renovated the Souk. At the end of the Bab Sharqi street, one reaches the House of Ananias, an underground chapel that was the cellar of Ananias's house. The Umayyad Mosque, also known as the Grand Mosque of Damascus, is one of the largest mosques in the world and also one of the oldest sites of continuous prayer since the rise of Islam. A shrine in the mosque is said to contain the body of St. John the Baptist. The mausoleum where Saladin was buried is located in the gardens just outside the mosque. Sayyidah Ruqayya Mosque, the shrine of the youngest daughter of Husayn ibn Ali, can also be found near the Umayyad Mosque. Another heavily visited site is Sayyidah Zaynab Mosque, where the tomb of Zaynab bint Ali is located.
Shia/fatemid/dawoodi bohra believe that after Karbala battle(680) Ummayad caliph Yazid brought Imam Husain 's head in Damascus, it was first buried in the courtyard of Umayyad Mosque yezid mahal ,shrine of the same still exist(see photo of the renovated shrine at right) . All other remaining member of husain's Family (left live after Karbala battle)along with heads of all other companions, who were killed at Karbala were also brought to Damascus,sham. These members were kept as prisoner at outskirt of city (Near Bab al-Saghir) ,the other heads were buried at the same location , now called "Raous-us-sohda-e-karbala " (photo placed at right), now visited by all shia.There is qibla( place of worship) marked at place, where Imam Ali-Zain-ul-Abedin use to pray under this captivity (pl.see photo,right). These are very important Islamic historical incident related with Damascus.
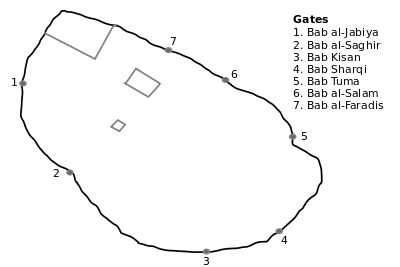
The walls and gates of Damascus
 Azm Palace
Damascus
Citadel Umayyad Mosque
|
| Gates |
| al-Jabiya · al-Saghir · Kisan · Sharqi · Tuma · al-Salam · Faradis |
The Old City of Damascus is surrounded by ramparts on the northern and eastern sides and part of the southern side. There are seven extant city gates, the oldest of which dates back to the Roman period. These are, clockwise from the north of the citadel:
- Bab al-Saghir (The Small Gate)
- Bab al-Faradis ("the gate of the orchards", or "of the paradise")
- Bab al-Salam ("the gate of peace"), all on the north boundary of the Old City
- Bab Tuma ("Touma" or "Thomas's Gate") in the north-east corner, leading into the Christian quarter of the same name,
- Bab Sharqi ("eastern gate") in the east wall, the only one to retain its Roman plan
- Bab Kisan in the south-east, from which tradition holds that Saint Paul made his escape from Damascus, lowered from the ramparts in a basket; this gate is now closed and a chapel marking the event has been built into the structure,
- Bab al-Jabiya at the entrance to Souk Midhat Pasha, in the south-west.
Other areas outside the walled city also bear the name "gate": Bab al-Faraj, Bab Mousalla and Bab Sreija, both to the south-west of the walled city.
Churches in the old city
- Mariamite Cathedral of Damascus.
- House of Saint Ananias.
- Chapel of Saint Paul.
- The Roman Catholic Cathedral in Zaitoon (Olive) Alley.
- The Damascene Saint Johan church.
- Saint Paul's Laura.
- Saint George's Syriac Orthodox Church.
 House of Saint Ananias |
 A church in the old city |
 Saint George's Syriac Orthodox Church. |
Islamic sites in the old city
- Sayyidah Zaynab Mosque
- Sayyidah Ruqayya Mosque
- Bab Saghir cemetery
- Umayyad Mosque
- Saladin Shrine.
 Bāb Saghīr Cemeteries,having shrine of Sakina binte Husain etc |
Sayyidah Zaynab-ul Kubra Mosque |
Sayyidah Ruqayya Mosque |
Madrasas

- Al-Adiliyah Madrasa.
- Az-Zahiriyah Library.
- Nur al-Din Madrasa.
Old Damascene houses
- Azm Palace
- Bayt al-Aqqad (Danish Institute in Damascus)
- Maktab Anbar
- Beit al-Mamlouka (Boutique Hotel)
Khans

- Khan Jaqmaq
- Khan As'ad Pasha
- Khan Sulayman Pasha
Threats to the future of the old City
Due to the rapid decline of the population of Old Damascus (between 1995–2005 more than 20,000 people moved out of the old city for more modern accommodation), a growing number of buildings are being abandoned or are falling into disrepair. In March 2007, the local government announced that it would be demolishing Old City buildings along a 1,400-metre (4,600 ft) stretch of rampart walls as part of a redevelopment scheme. These factors resulted in the Old City being placed by the World Monuments Fund on its 2008 Watch List of the 100 Most Endangered Sites in the world. It is hoped that its inclusion on the list will draw more public awareness to these significant threats to the future of the historic Old City of Damascus.
Current state of old Damascus
In spite of the recommendations of the UNESCO World Heritage Center:[58]
- Souk El Atik, a protected buffer zone, was destroyed in three days in November 2006;
- King Faysal Street, a traditional hand-craft region in a protected buffer zone near the walls of Old Damascus between the Citadel and Bab Touma, is threatened by a proposed motorway.
- In 2007, the Old City of Damascus and notably the district of Bab Tuma have been recognized by The World Monument Fund as one of the most endangered sites in the world.[59]
Subdivisions


Damascus is divided into many districts. Among them there are:
- Abbasiyyin
- Abu Rummaneh
- Amara
- Bahsa
- Baramkah
- Barzeh
- Dummar
- Jobar
- Kafar Souseh
- Malki
- Mazraa
- Mezzeh
- Midan
- Muhajreen
- Qanawat
- Rukn Eddeen
- Al-Salihiyah
- Sarouja
- Sha'alan
- Al-Shaghour
- Tijara
Education

Damascus is the main center of education in Syria. It is home to Damascus University, which is the oldest and largest university in Syria. After the enactment of legislation allowing private secondary institutions, several new universities were established in the city and in the surrounding area, including:
- Syrian Virtual University
- International University for Science and Technology
- Higher Institute of Business Administration
- Higher Institute for Applied Science and Technology
- University of Kalamoon
- Arab International University
- National Institute of Administration
Transportation



The main airport is Damascus International Airport, approximately 20 km (12 mi) away from the city center, with connections to many Asian, European, African, and recently, South American cities. Streets in Damascus are often narrow, especially in the older parts of the city, and speed bumps are widely used to limit the speed of vehicles.
Public transport in Damascus depends extensively on minibuses. There are about one hundred lines that operate inside the city and some of them extend from the city center to nearby suburbs. There is no schedule for the lines, and due to the limited number of official bus stops, buses will usually stop wherever a passenger needs to get on or off. The number of buses serving the same line is relatively high, which minimizes the waiting time. Lines are not numbered, rather they are given captions mostly indicating the two end points and possibly an important station along the line.
Served by Chemins de Fer Syriens, the former main railway station of Damascus was al-Hejaz railway station, about 1 km west of the old city. The station is now defunct and the tracks have been removed, but there still is a ticket counter and a shuttle to Damacus Kadam station in the south of the city, which now functions as the main railway station.
In 2008, the government announced a plan to construct a Damascus Metro with opening time for the green line scheduled for 2015.[60] The green line will be an essential West-East axis for the future public transportation network, serving Moadamiyeh, Sumariyeh, Mezzeh, Damascus University, Hijaz, the Old City, Abbassiyeen and Qaboun Pullman bus station. A four-line metro network is expected be in operation by 2050.
Culture
Damascus was chosen as the 2008 Arab Capital of Culture. The Arab Capital of Culture is an initiative undertaken by UNESCO,[61] under the Cultural Capitals Program to promote and celebrate Arab culture and encourage cooperation in the Arab region. The preparation for the festivity began in February 2007 with the establishing of the Administrative Committee for “Damascus Arab Capital of Culture" by a presidential decree.[62]
Syrian Cuisine
The Syrian cuisine is rich and varies in its ingredients which is linked to the region of Syria where a specific dish has originated. The main dishes are kibbeh, wara' enab, hummus, tabbouleh, fattoush, labneh, shawarma, mujaddara, shanklish, pastırma, sujuk and ba'lawa. Ba'lawa is made of filo pastry filled with chopped nuts and soaked in honey. Syrians often serve selections of appetizers, known as meze, before the main course. za'atar, minced beef, and cheese manakish are popular hors d'oeuvres. The Arabic flatbread khubz is always eaten together with meze. Syrians are also well-known for their cheese. The very popular string cheese jibbneh mashallale is made of curd cheese and is pulled and twisted together. Syrians also make cookies to usually accompany their cheese called ka'ak. These are made of farina and other ingredients, rolled out, shaped into rings and baked. Another form of a similar cookie is to fill with crushed dates mixed with butter to accompany their jibbneh mashallale. Drinks in Syria vary depending on the time of the day and the occasion. Arabic coffee, also known asTurkish coffee is the most well-known hot drink usually prepared in the morning at breakfast or in the evening. it is usually served for guests or after food. Alcoholic drink Arak is also a well-known beverage served mostly in occasions. more examples of Syrian beverages include Ayran, Jallab, and White coffee. there is also a well-known locally manufactured beer called Al Shark.[63]
Museums
- National Museum of Damascus
- Azem Palace
- Military Museum
- October war Panorama Museum
- Museum of Arabic Calligraphy
- Nur al-Din Bimaristan
- The Museum of Shahbah
|
National Museum of Damascus |
 October War Panorama Museum |
Sports
Popular sports include football, basketball, swimming and table tennis. Damascus is home to many sports clubs, including Al Jaish, Al Wahda and Al Majd.
The fifth and the seventh Pan Arab Games were held in Damascus in 1976 and 1992, respectively.
Leisure activities

Coffeehouses, where—in addition to Arabic coffee and tea—hookahs (water pipes) are served, proliferate Damascus. Card games, tables (backgammon variants), and chess are activities frequented in cafes.[64]
Tishreen Park is by far the largest park in Damascus. It is home to the yearly held Damascus Flower Show. Other parks include Aljahiz, Al sibbki, Altijara and Alwahda. Damascus' Ghouta (Oasis) is also a popular destination for recreation. There are several recreation centers in Damascus including several stadiums, swimming pools and golf courses. Also, The Syrian Arab Horse Association in Damasacus offers a wide range of activities and services for horse breeders and riders.[65]
Nearby attractions
- Madaya: a small mountainous town well known holiday resort.
- Bloudan: a town located 51 km north-west of the Damascus, its moderate temperature and low humidity in summer attracts many visitors from Damascus and throughout Syria, Lebanon and the Arab Gulf.
- Zabadani: a city in close to the border with Lebanon. Its mild weather along with the scenic views, made the town a popular resort both for tourists and for visitors from other Syrian cities.
- Maaloula: a town dominated by speakers of Western Neo-Aramaic.
- Saidnaya: a city located in the mountains, 1,500 metres (4,921 ft) above sea level, it was one of the episcopal cities of the ancient Patriarchate of Antioch.
Twin towns and sister cities
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Syrian News Agency: Syrian Population Estimated at 19,405 Million
- ↑ Albaath.news statement by the governor of Damascus, Syria (Arabic, April 2010
- ↑ "Syria". State.gov. 2010-02-17. http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/3580.htm. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ "دمشق عاصمة الثقافة العربية 2008". Damascus.org.sy. http://damascus.org.sy/. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ List I, 13 in J. Simons, Handbook for the Study of Egyptian Topographical Lists relating to Western Asia, Leiden 1937. See also Y. AHARONI, The Land of the Bible: A Historical Geography, London 1967, p147, No. 13.
- ↑ "(in Book Reviews) ''Ancient Damascus: A Historical Study of the Syrian City-State from Earliest Times Until Its Fall to the Assyrians in 732 BCE.'', Wayne T. Pitard. Review author: Paul E. Dion, ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', No. 270, Ancient Syria. (May, 1988), p. 98". Links.jstor.org. http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0003-097X%28198805%290%3A270%3C97%3AADAHSO%3E2.0.CO%3B2-S. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ "''The Stele Dedicated to Melcarth by Ben-Hadad of Damascus'', Frank Moore Cross. ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', No. 205. (Feb., 1972), p. 40". Links.jstor.org. http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0003-097X%28197202%290%3A205%3C36%3ATSDTMB%3E2.0.CO%3B2-9. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ "Online Etymology Dictionary". Etymonline.com. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=Damascus. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ "Damascus – Wiktionary". En.wiktionary.org. 2010-05-09. http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Damascus. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ Moore, A.M.T. The Neolithic of the Levant. Oxford, UK: Oxford University, 1978. 192–198. Print.
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 2
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Burns 2005, pp. 5–6
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Burns 2005, p. 7
- ↑ Genesis 14:15 (New International Version), Bible Gateway, http://www.biblegateway.com/passage/?search=Genesis%2014:15&version=NIV, retrieved 25 November 2009
- ↑ MacMillan, pp. 30–31
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 9
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Burns 2005, p. 10
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 13–14
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Burns 2005, p. 11
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 21–23
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 98–99
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 100
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 103–104
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 105
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 106–107
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 110
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 113
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 121–122
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 130–132
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 135–136
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 137–138
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 139
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 142
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 147
- ↑ Burns 2005, pp. 148–149
- ↑ Burns 2005, p. 151
- ↑ Jonathan Phillips, The Second Crusade: Extending the Frontiers of Christendom (Yale University Press, 2007), pp. 216–227.
- ↑ Hans E. Mayer, The Crusades (Oxford University Press, 1965, trans. John Gillingham, 1972), pp. 118–120.
- ↑ Christopher Tyerman, God's War: A New History of the Crusades (Penguin: 2006), p. 350.
- ↑ Bernard Hamilton, The Leper King and his Heirs: Baldwin IV and the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem (Cambridge University Press, 2000), pp. 132–136.
- ↑ "The Third Crusade: Richard the Lionhearted and Philip Augustus", in A History of the Crusades, vol. II: The Later Crusades, 1189–1311, ed. R. L. Wolff and H. W. Hazard (Madison, Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin Press, 1969), pp. 45–49.
- ↑ Wolff and Hazard, pp. 67–85.
- ↑ Islamic city. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ↑ Ellen Clare Miller, 'Eastern Sketches – notes of scenery, schools and tent life in Syria and Palestine'. Edinburgh: William Oliphant and Company. 1871. page 90. quoting Eli Jones, a Quaker from New England.
- ↑ Barker, A. (1998)"The Allies Enter Damascus", History Today, Volume 48
- ↑ Roberts, P.M., World War I, a Student Encyclopedia, 2006, ABC-CLIO, p.657
- ↑ Tyson, Patrick J. (2003), SUNSHINE GUIDE TO THE DAMASCUS AREA, SYRIA, www.climates.com, http://www.climates.com/ASIA/PDF/SYR02ASA.pdf, retrieved 26 November 2009
- ↑ World Weather Information Service – Damascus, http://worldweather.wmo.int/099/c00213.htm
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 49.4 49.5 "Damascus". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/150420/Damascus. Retrieved 2009-11-28.
- ↑ "Damascus International Fair". http://www.peife.gov.sy. Retrieved 2009-11-28.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 "Damascus Revels in Its New Allure to Investors". The Wall Street Journal. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB125841487085151317.html. Retrieved 2009-11-28.
- ↑ "Report: Office Space Across the World 2009". Cushman & Wakefield. http://www.cushwake.com/cwglobal/jsp/kcReportDetail.jsp?Country=GLOBAL&Language=EN&catId=100003&pId=c21200007p. Retrieved 2009-11-28.
- ↑ "Inauguration of Damascus Stock Exchange". Syrian Enterprise and Business Center. http://www.sebcsyria.com/web2008/art.php?art_id=1619. Retrieved 2009-11-28.
- ↑ (AFP) – Mar 10, 2009 (2009-03-10). "AFP: Syria launches first stock exchange". Google.com. http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5gPsB6CSsyXUgWdxEsC0B_O-jqV-w. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ Central Bureau of Statistics General Census of Population and Housing
- ↑ Flood, Finbarr Barry (2001), The Great Mosque of Damascus: studies on the makings of an Umayyad visual culture, 33, BRILL, p. 12, ISBN 9004116389, 9789004116382, http://books.google.com/?id=r5f8kxIyykQC&printsec=frontcover&q=, retrieved 2009-11-26
- ↑ Katz, Ketsi'ah (1981), Masoret ha-lashon ha-'Ibrit shel Yehude Aram-Tsoba (Ḥalab) bi-qri'at ha-Miqra ve-ha-Mishnah (The Hebrew Language Tradition of the Jews of Aleppo in the Reading of the Bible and Mishnah)
- ↑ The British Syrian Society, The British Syrian Society, http://www.britishsyriansociety.org/dam2020/recommendations.asp, retrieved 2009-05-29
- ↑ Worldmonuments.org
- ↑ الخط الأخضر » أهلاً بكم في موقع الخط الأخضر, Damascus-metro.com, http://www.damascus-metro.com, retrieved 2009-05-29
- ↑ Herbert, Ian; Nicole Leclercq, International Theatre Institute (2003), The World of Theatre: An Account of the World's Theatre Seasons 1999–2000, 2000–2001 and 2001–2002, Routledge, p. 225, ISBN 0415306213
- ↑ "مجلس الإدارة و المجلس الاستشاري". Damascus.org.sy. 2007-10-22. http://damascus.org.sy/?d=298. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ Damascus, RTÉ, 2009-10-15, http://www.rte.ie/travel/2009/1015/damascus.html, retrieved 26 November 2009
- ↑ Beatties and Pepper, 2001, p. 102.
- ↑ "Syrian Arab Horse Association". Saha-sy.org. http://www.saha-sy.org/. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ UAEinteract.com, Sister Cities delegates praise Dubai 'best practices' UAE – The Official Web Site – News, Uaeinteract.com, http://uaeinteract.com/docs/Sister_Cities_delegates_praise_Dubai_best_practices/12110.htm, retrieved 2009-05-29
- ↑ "Sister Cities", Toledo Turismo (Patronato Municipal de Turismo), http://www.toledo-turismo.com/turismo/contenido/mas-toledo/toledo-historia/ciudades-hermanadas.aspx, retrieved 2008-10-16
- ↑ Conventions of brotherhood and friendship signed between the city of Cairo and the Arab Towns, Cairo Governorate, http://www.cairo.gov.eg/txtlstvw.aspx?LstID=3aa2ef76-956d-438f-95eb-d280f15d00b2, retrieved 2009-11-28
- ↑ "Athens mayor concludes four-day visit to Syria." Europe Intelligence Wire. Financial Times Ltd. 2004. AccessMyLibrary. 28 Nov. 2009 <http://www.accessmylibrary.com>.
- ↑ Syrian Press: 09 July 2008, Syrian Arab News Agency, http://translate.google.ca/translate?hl=en&sl=ar&u=http://www.sana.sy/print.html%3Fsid%3D183236%26newlang%3Dara&ei=qmITS-21AYzStgOfudHCAQ&sa=X&oi=translate&ct=result&resnum=7&ved=0CCIQ7gEwBg&prev=/search%3Fq%3D%25D8%25AF%25D9%2585%25D8%25B4%25D9%2582%2B%25D8%25A8%25D8%25AE%25D8%25A7%25D8%25B1%25D8%25B3%25D8%25AA%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG, retrieved 2009-11-29
- ↑ La Cooperación Directa en el Ayuntamiento de Córdoba – Córdoba City Council Web
- ↑ Prefeitura.Sp – Descentralized Cooperation
- ↑ "International Relations – São Paulo City Hall – Official Sister Cities". Prefeitura.sp.gov.br. http://www.prefeitura.sp.gov.br/cidade/secretarias/relacoes_internacionais/cidadesirmas/index.php?p=1066. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ Yerevan Municipality – Sister Cities, © 2005–2009 www.yerevan.am, http://yerevan.am/main.php?lang=3&page_id=194, retrieved 2009-06-22
- ↑ Sister Cities of Istanbul – Turkey, Sister Cities of Istanbul – Turkey, http://www.greatistanbul.com/sister_cities.htm, retrieved 2009-11-24
- ↑ اتفاقية توءمة بين دمشق واسطنبول Twining agreement between Damascus and Istanbul, The New Alphabet/SANA, http://translate.google.ca/translate?hl=en&sl=ar&u=http://www.thenewalphabet.com/details1138.html&ei=l2gTS6W7Lon8sQPOjazCAQ&sa=X&oi=translate&ct=result&resnum=2&ved=0CAwQ7gEwAQ&prev=/search%3Fq%3D%25D8%25AA%25D9%2588%25D8%25A1%25D9%2585%25D8%25A9%2B%25D8%25AF%25D9%2585%25D8%25B4%25D9%2582%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG, retrieved 2009-11-29
- ↑ A turning positive ... President Assad: Our conversations rich narratives and aspirations ... President Nazarbayev: We look forward to the partnership on the international arena ... Signed (4) agreements for bilateral cooperation, Alwehda Publications/SANA, http://translate.google.ca/translate?hl=en&sl=ar&u=http://thawra.alwehda.gov.sy/_archive.asp%3FFileName%3D102673524820071106025223&ei=TG4TS5TgCIuotgPWjLXmAQ&sa=X&oi=translate&ct=result&resnum=9&ved=0CCsQ7gEwCDgU&prev=/search%3Fq%3Dsite:thawra.alwehda.gov.sy%2B%25D8%25AA%25D9%2588%25D8%25A1%25D9%2585%25D8%25A9%2B%25D8%25AF%25D9%2585%25D8%25B4%25D9%2582%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DN%26start%3D20, retrieved 2009-11-29
- ↑ The Syrian-Iranian Joint Supreme Committee meetings ..., Alwehda Publications, http://translate.google.com/translate?js=y&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&u=http%3A%2F%2Fthawra.alwehda.gov.sy%2F_print_veiw.asp%3FFileName%3D20193318520090307225758&sl=ar&tl=en, retrieved 2009-11-30
- ↑ محافظة دمشق ومنطقة نينغيشيا الصينية توقعان على اتفاقية توأمة, Syria News, http://www.syria-news.com/readmynews.php?sy_seq=113554, retrieved 2010-04-22
Bibliography
- Burns, Ross (2005), Damascus: A History, Routledge, ISBN 0415271053, 9780415271059, http://books.google.com/?id=1_bQTrpf62cC&dq=damascus.
- Jill, Duchess of Hamilton (2002), First to Damascus: The story of the Australian Light Horse and Lawrence of Arabia, ISBN 0-7318-1071-6.
- Aharoni, Yohanan; Avi-Yonah, Michael (1977), The MacMillan Bible Atlas, Carta Ltd., ISBN 0-7318-1071-6.
- Cammelli, Stefano (2006), Il Minareto di Gesù, Il Mulino.
- ICOMOS Heritage at Risk 2001/2002: Damascus, A Major Eastern Mediterranean Site at Risk
- Syria, Historic Damascus: The Destruction of the Old City
External links
- Ernst Herzfeld Papers, Series 5: Drawings and Maps, Records of Damascus Collections Search Center, S.I.R.I.S., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
- eDamascus – Official website for Damascus
- Damascus Online – Brief information about the city of Damascus
- The 31 Places to Go in 2010 (The New York Times)
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
|||||